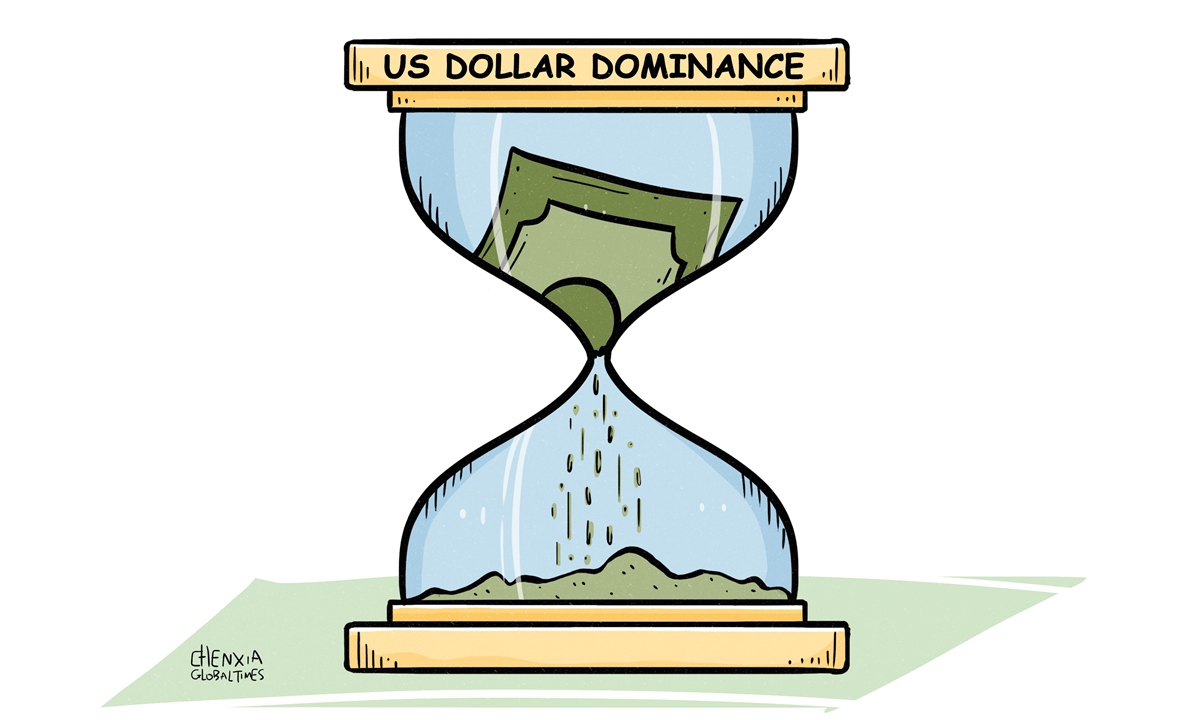
Is the Dollar the key to US hegemony?

Illustration:Chen Xia/Global Times
The US Federal Reserve will hold a new policy meeting on Tuesday and Wednesday, with the decision on interest rate growth being the limelight. It is widely anticipated that the Fed will deliver at least another 75-basis-point interest rate hike to tame inflation. This might further increase the value of the US dollar against other currencies, which is at its 20-year high. Driven by the Fed's aggressive rate hikes, the US dollar is viewed as "experiencing a once-in-a-generation rally." For many countries in the world, this might be the beginning of another nightmare. The meeting will witness the fifth time that the Fed will raise interest rates. The direct reason is to ease the high pressure of inflation in the US. But if people dig the root cause, this is an inevitable consequence of US' blind and unlimited money printing to temporarily maintain "prosperity." In other words, in the face of the deep-seated problems exposed by the 2008 financial crisis, Washington has been powerless, and unwilling as well, to solve them. Instead, it was extremely short-sighted to cover up the crisis and curry favor with the Wall Street, while taking advantage of the hegemony of the US dollar to quietly treat the crisis like dumping wastewater - draining it to the world. A super strong US dollar and the fall of other currencies will, to a certain extent, ease the scorching inflation in the US economy, but the world will have to pay for it, which is often referred to as "when the US is sick, the world has to takes pill." The ensuing severe inflation, economic recession and other problems have already appeared on a large scale in many countries. Thirty-six currencies around the world have lost at least one-tenth of their value this year, with the Sri Lankan rupee and Argentine peso falling by more than 20 percent, since the dollar strengthened. This has not only worsened the already weak economies of Europe and Japan, but also forced a large number of developing countries to swallow the bitter pills of the economic recession caused by imported inflation. Countless families were impoverished overnight. This is a very abnormal situation that is not supposed to occur, but it is the cruel truth behind the US "containment of inflation." In fact, since the end of World War II, the US has used dollar hegemony to carry out "financial looting" or "export crises" against other countries several times. As a widely popular phrase in the West goes, the US enjoys the exorbitant privileges created by the dollar and the deficit without tears, and used the worthless paper note to plunder the resources and factories of other nations. Each round of dollar appreciation in the past decades has been accompanied by extremely bad memories: The Latin American debt crisis broke out in the first round, Japan suffered from the "lost two decades" during the second round and the Asian financial crisis took place during the third. Particularly in the Asian crisis, which is still fresh in many people's memories, more than 100 million middle-class people in Asia fell into poverty, according to the World Bank estimation. The strengthened dollar, time and again, cuts the world like a sharp blade. Therefore, while the political elites in Washington boast of the "myth of the American system" and take credit for "alleviating the crisis," thousands of poor families around the world are being trampled by them. They are not unaware of this, but still collectively choose to be indifferent and arrogant, as if this is the privilege that the "hegemon" should enjoy. As US former treasury secretary John Connally put it in the 1970s, "The dollar is our currency, but it's your problem." Today, the dollar is once again the world's problem. In a sense, it's hard to believe that the "prosperity" of the US is clean and moral. However, the crisis cannot be covered up forever. Washington keeps laying mines but never removes them, which will eventually explode the US itself. The incompetence of US financial policymakers has been exposed by the consecutive interest rate hikes that have contributed to the abnormal appreciation of the US dollar with the purpose of defusing the severe inflation. For the US itself, what will rise accordingly are the cost of corporate financing, the pressure on residents to repay their loans, and the price of export production among others. Meanwhile, the credibility that the US dollar has as a global currency is being continuously exhausted by the US "beggar-thy-neighbor" policy. Now the anxiety and insecurity brought by the US dollar to the world has heralded the beginning of the decline of its hegemony - regarding Washington's insatiable exploitation, Europe, Asia, the Middle East and other regions have explored the path of "de-dollarization," leading to the inevitable diversification of the international monetary system.
The best way to restrain the rampaging hegemony is to practice true multilateralism. Whether it was the Asian financial crisis in 1997 or the global financial crisis in 2008, the world seemed to have stumbled more than once by the same stone, which, however, is not that firm anymore. The instability and fragility of international financial markets have once again become prominent. It is precisely at such times that the international community should be more determined to cooperate and build a reliable, systemic and long-term multilateral international financial system. This cannot wait.
THE NEED FOR BRETTON WOODS III
World Affairs – Non-Partisan and Objective

Why the US Needs to Destroy Russia and China — The Need for Bretton Woods III
The United States of America is in big trouble, short term and long term. In 2022, the stock market is crashing, bond market is down the most in 40 years, housing bubble is bursting, inflation is skyrocketing, debt is exploding, and GDP is shrinking. These are not temporary crises. Instead, they reveal systemic flaws in the American economy that is propped up by a rigged global financial system.
However, that fraudulent system is starting to crumble and the primacy of US dollar is in serious trouble, thanks to an emerging multipolar world. (Don't believe the nonsense that the US can keep printing infinite amount of dollars).
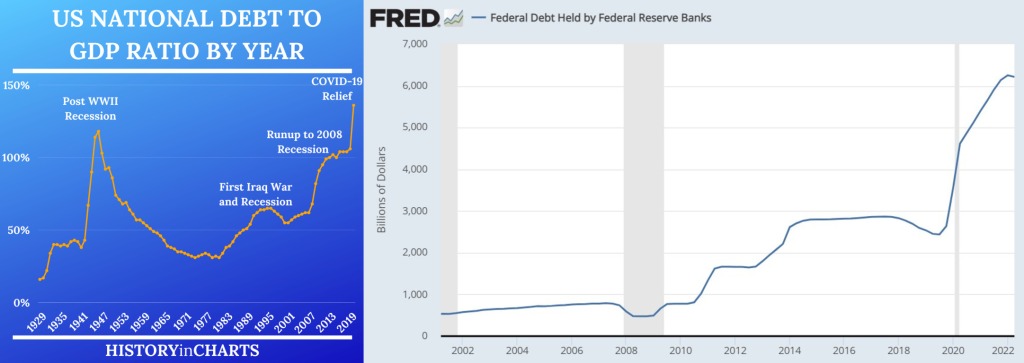
US central government’s debt is now $31 trillion, amounting to 130% of GDP. Soon, the interest payments on the debt alone will be $1 trillion per year. Of course, the principal amount will never get paid off. Then, add in the unfunded liabilities — like future payments for social security — the debt is staggering over $200 trillion.
Furthermore, there are not enough buyers of US treasuries. Thus, since the 2008 financial crisis, the Federal Reserve Bank has been creating trillions of dollars literally out of thin air and buying the US debt (treasury bonds). This is voodoo economics and not sustainable.
What’s the end game? The US needs to default on its debt and start new. The goal is to declare bankruptcy and … yet remain the #1 country. This will be the “Bretton Woods III” agreement.
The US needs to default on its debt and start new. Declare bankruptcy and yet remain the #1 country. This will be the "Bretton Woods III" agreement. Sounds ridiculous? Well, it's possible only if all the other countries are weak and nobody is strong enough to challenge the US. This is why the US must not only crush Russia and China — its two biggest geopolitical rivals, but also weaken Europe. This paves the way for the US to establish a new global order which is similarly rigged and just as deceitful and corrupt — in order to prolong the American Century. Dollar Hegemony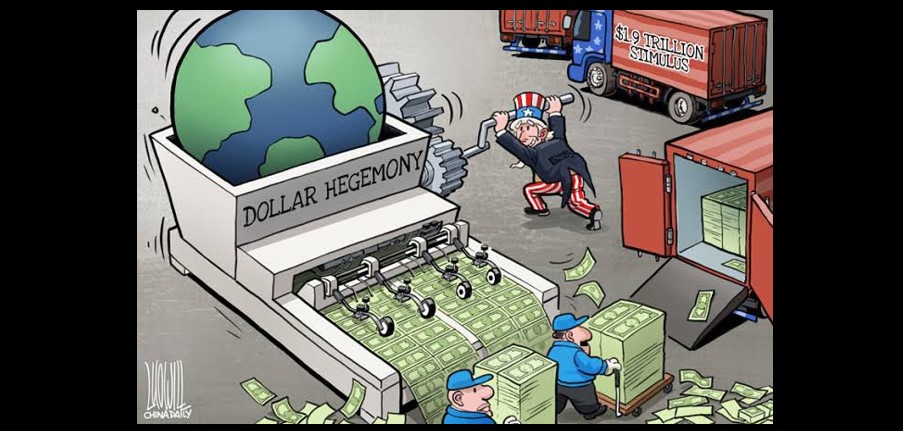
America's extraordinary power comes from the power of US dollar, which is the established global currency for trade. This also means that countries around the world have to accumulate US dollars in their foreign exchange reserves. But the US has been abusing its power by weaponizing the dollar through sanctions and confiscations of hard-earned reserves.
No wonder that China, Russia and others are seeking ways to circumvent the dollar in trade. Since 1999, the share of US dollar assets in central bank reserves has dropped by 12 percentage points—from 71 percent. Hence the share of US dollar in global reserves is now only 59%. When that number falls below 50%, the tectonic shifts in global finance will become more apparent to Americans. To fully grasp the nature of the current world order, let's see how the US established the dollar as the world currency, carried about the biggest gold heist in human history, then defaulted on its obligations, but revived the moribund dollar with a clever deal. That's the story of Bretton Woods I and II. Bretton Woods I - Gold-backed Dollar WW2 was a wonderful thing for the US. First, it took the US economy out of the Great Depression. The US played the role of arms supplier and gladly watched European empires destroy themselves. Even before the war was over, the US brought in all the allies to Bretton Woods, New Hampshire, and said, "When the war is over, you will all be weak and broke. I will be the new empire and my dollar will be the global currency. And it will be as good as gold -- a guaranteed rate of $35 per ounce of gold." This meant that if you have $35, you can go to a bank and get an ounce of gold! The world agreed. When the war was over, everyone bought US dollar with gold and used it for trade. Huge amounts of gold were also physically transferred from Japan, Germany and other parts of the world into the vaults of the Federal Reserve Bank in New York. This system worked until 1971 when the US suddenly declared that, "Oops, the dollar is not backed by gold anymore. If you have US dollars, they are just pieces of paper now. You cannot get your gold back!" People called it the "Nixon Shock." 1970s - When Fiat Dollar almost died This was also the biggest gold theft in human history. But what could the world do? America had nuclear weapons and the mightiest military.Of course, the switch to a fiat currency caused havoc. The value of US dollar fell precipitously and inflation skyrocketed. Oil price quickly doubled and grew five-fold by 1979. The oil shock and gas shortage rocked American politics.

The US economy was in deep trouble. That's when the US elites came up with a clever idea to rescue the dollar and restore its primacy.
Bretton Woods II - The Birth of Petrodollar How to make the dollar relevant? Hmm...What if everyone needed US dollar to buy something essential? Like ... OIL. Brilliant! This was the birth of Petrodollar.Basically, the U.S. used Saudi Arabia’s oil to save the dollar. That is, Saudi Arabia (and other smaller producers) would sell oil only for US dollars. And to make sure that the Saudis don't get too powerful, they will be forced to recycle most of their profits back into the US economy. It was also a protection racket, which meant the US military would occupy Saudi Arabia and protect it from enemies.
 Saudi King Faisal with Kissinger. Birth of Petrodollar
Saudi King Faisal with Kissinger. Birth of Petrodollar
But why would the Saudis agree to this? Because the U.S. make Saudi Arabia the new king of oil and the most influential Middle East power ... after crippling Iran.
Win-win for the US.Thus, the U.S. armed and funded Saddam Hussein of Iraq to wage a decade-long war on Iran. US provided arms/intelligence. Germany and France provided deadly chemical/biological weapons to Iraq. Here’s Donald Rumsfeld with Saddam in 1983.

In the most optimistic scenario, the Global South or the people of the developing nations can bring into fruition a new fair world without catastrophic wars or financial devastation. As Sun Tzu said, "The supreme art of war is to subdue the enemy without fighting."
 Rising calls for increased yuan use in C.Asia amid growing risk of dollar hegemony
Rising calls for increased yuan use in C.Asia amid growing risk of dollar hegemony
Companies attending the 7th China-Eurasia Expo in Urumqi, Northwest China's Xinjiang region said the increased use of the yuan in cross-border trade in Central Asia is making business more convenient and reducing foreign exchange risks stemming from the use of the US dollar, and they called for more arrangements to ...
Related posts:
Whither the ringgit? US Inflation & workforce are the bigger problems
















 https://www.abc.net.au/news/2022-09-18/queen-elizabeth-ii-empire-colonialism-history/101430296
https://www.abc.net.au/news/2022-09-18/queen-elizabeth-ii-empire-colonialism-history/101430296







